The quote “Fool me once, shame on you” is the beginning of a longer saying that goes, “Fool me once, shame on you; fool me twice, shame on me.” In essence, the quote emphasizes the importance of learning from one’s mistakes and not allowing oneself to be taken advantage of repeatedly. It’s a call to be cautious and to recognize patterns of deceit or betrayal. But is this impossible within the stock market?
Those of longer standing in the investment world will realize that no matter how smart we claim to be, we fall for the same mistakes again. They just come in different disguises. I often say that the stock market isn’t a machine for making money; it was inherently set up to fool you.
One of my favorite books on the subject is “Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds” by Charles Mackay, which was originally published in 1841. This book digs at the psychology behind mass hysteria, asking why so many individuals at once can hold such implausible beliefs. The South Sea Bubble, the Dutch tulip craze, and the Mississippi Scheme are just a few of the historical financial disasters that Mackay describes. Mackay uses these historical instances to demonstrate the recurrent character of such crises and the collective folly that can lead to the financial collapse of a civilization. This book serves as a warning against the perils of herd mentality and the prevalence of mass hysteria based on hearsay.
In the book, important economic bubbles are discussed. Also, from the religious fervor of the Crusades and the hysteria of witch hunts to the mystery of alchemy and prophecy, it examines a wide range of prevalent beliefs and obsessions. Mackay cites examples like Dancing Mania and the belief in haunted houses to show how common collective illusions are and how irrational mass behavior can be. I’d urge you to read this book as a part of your learning process.
History Continues To Fool Us
There have been numerous financial scandals throughout the past century. During the 1920s, government officials were implicated in the Teapot Dome Scandal for leasing Navy petroleum reserves to private oil businesses through fraudulent means. When regulators in the 1970s terminated the license of the Herstatt Bank, it generated chaos in the foreign exchange market. After the Enron crisis of 2001 exposed massive accounting fraud, Arthur Andersen, one of the world’s five largest audit and accounting partnerships, disintegrated. Bernie Madoff was caught in 2008 for running the largest known Ponzi scheme, which defrauded thousands of people. In 2015, Volkswagen shocked the car industry by altering engine software to cheat pollution testing. Lawmaking, investor confidence, and business practices were all significantly impacted by these occurrences. These scandals can all be related to Mackay’s work.
Why Are We Fooled?
Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts people use to make decisions faster. Although these biases simplify our thinking, they can lead to mistakes. A famous example is confirmation bias, where people favor information that supports their beliefs and ignore contrary facts. Heuristics—general decision-making rules of thumb—can also be helpful and harmful. The representativeness heuristic encourages people to judge an event’s probability based on its likeness to a prototype, which may not be true. Emotions also have an impact on decisions. Fear of missing out (FOMO) can lead to rash stock investments without investigation. Humans’ quest for social acceptance can also cloud judgment. Even if they doubt the company’s future, someone may buy a popular stock to fit in. Finally, financial scammers use charm, urgency, and other strategies to trick people into giving over their money or personal information.
There are countless more examples, and the major ones are mentioned, but they continue. The basic, priceless tulip has come back as a technological one.
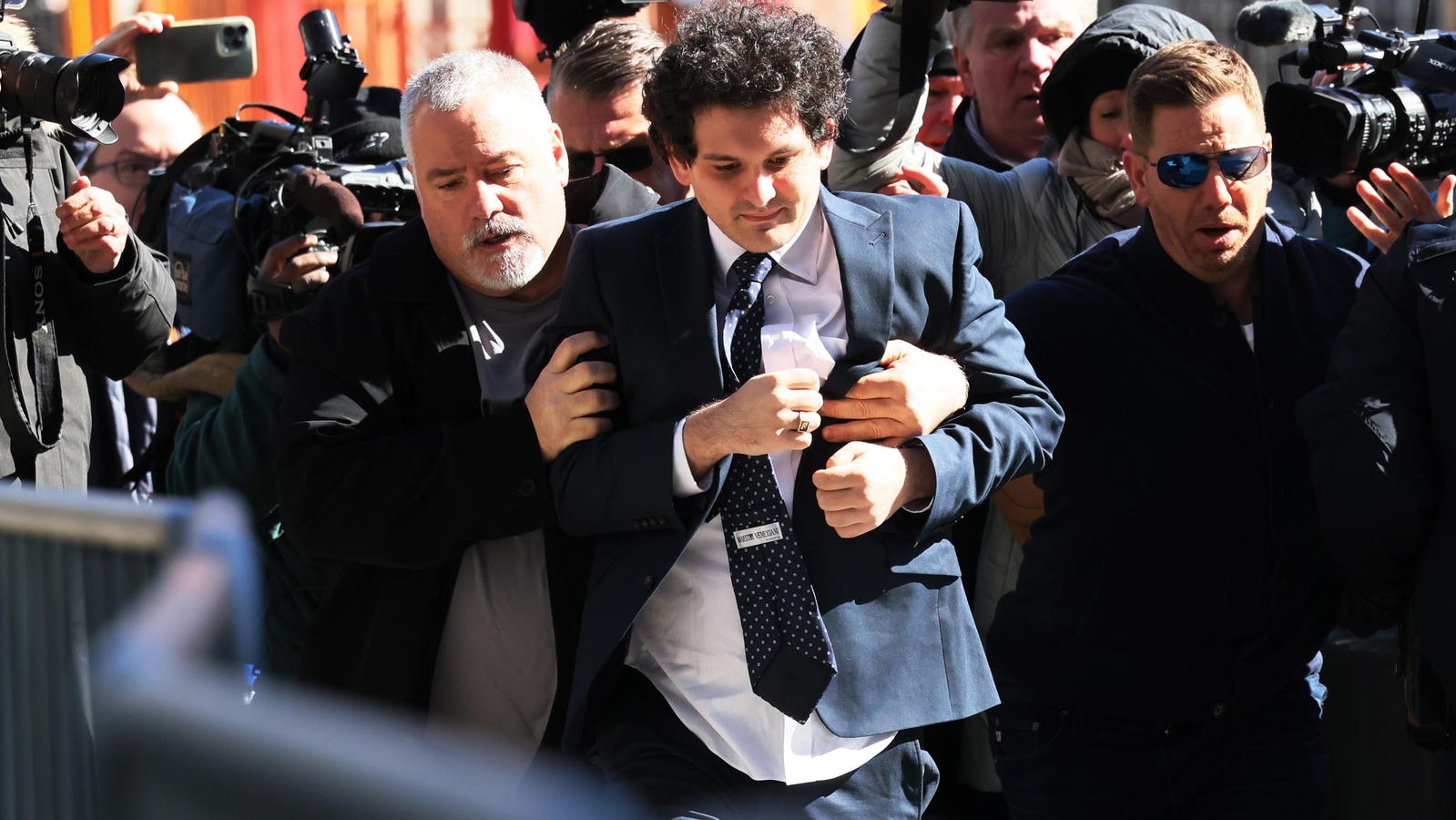
The FTX Scandal: The Charismatic Leader
In November 2022, the cryptocurrency exchange FTX, founded by Sam Bankman-Fried in 2019, faced a significant financial scandal leading to its collapse. Initially celebrated as a prodigy, Bankman-Fried’s mismanagement came to light when it was discovered that he used customer funds for personal luxuries and to support his other businesses. As concerns about FTX’s solvency grew, a massive wave of customer withdrawals ensued, which the platform couldn’t fulfill, resulting in its downfall. This event stands as one of the most substantial financial debacles in cryptocurrency history, inflicting billions in investor losses and tarnishing the industry’s reputation.
The scandal fits perfectly into Charles Mackay’s book. It is an illustration of how a charismatic leader and a guarantee of high returns can deceive people. Sam Bankman-Fried, the founder and CEO of FTX, was seen as a wunderkind in the crypto industry. He was able to raise billions of dollars from investors, including some of the biggest names in the tech world. Additionally, it serves as a reminder that even the most intelligent people are susceptible to deception by popular opinion.
However, Bankman-Fried’s promises of high returns were ultimately illusory. FTX was a poorly managed company, and it was eventually revealed that Bankman-Fried had been misusing customer funds. The company collapsed in November 2022, and investors lost billions of dollars.
Wirecard: Groupthink
The Wirecard controversy began in 2020 when Wirecard AG revealed that €1.9 billion in trustee accounts in the Philippines likely did not exist. After several Financial Times investigations into Wirecard’s accounting practices, this disclosure came. The corporation filed for insolvency after the scandal, one of Germany’s greatest post-war financial disasters. Markus Braun, the CEO, resigned and was arrested for fraud and market manipulation. Since Wirecard was a DAX
DAX
The Wirecard scandal is another concept conceptualized in Mackay’s work. It examines how societal manias can lead large groups of people to believe in and act upon illusions, often with detrimental consequences. Due to its apparent strong financials and inclusion in Germany’s DAX 30 stock index, Wirecard has experienced a rapid rise in the financial world, garnering significant investor interest and trust. However, under the surface, alleged fraudulent activities were hiding the company’s true financial health. When the truth about the missing €1.9 billion came to light, the once-celebrated company faced a dramatic downfall. Just as Mackay detailed historical bubbles and financial follies driven by collective delusion, the Wirecard incident serves as a modern testament to the dangers of unchecked enthusiasm.
Nikola Motors: Herd Mentality
In September 2020, Nikola Motors, founded in 2014 by Trevor Milton and claiming to develop electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles, faced a scandal when it was exposed for misleading investors about its technological progress. Despite attracting billions in investments, revelations emerged that a promotional video of a Nikola One truck was staged, with the truck merely rolling downhill, not powered by its own engine. Furthermore, the company lacked a working prototype and depended on third-party suppliers who hadn’t delivered essential parts. This deception led to a sharp decline in Nikola’s stock, Milton’s resignation, and investigations by regulatory bodies. By June 2023, Milton had been convicted of fraud and sentenced to four years in prison.
The rapid rise of Nikola Motors, driven by investor enthusiasm for its purportedly groundbreaking technology, mirrors the speculative bubbles and episodes of collective delusion that Mackay described. Investors were drawn to the company’s promises and the vision of its founder, Trevor Milton, without adequate scrutiny of its actual technological achievements. When the truth emerged, the bubble burst, leading to significant financial and reputational consequences. Just as Mackay highlighted historical instances of societal manias, the Nikola Motors scandal serves as a contemporary example of the dangers of herd mentality in financial markets and the importance of skepticism and due diligence.
Five Ways To Minimize Being Fooled
- Thorough Due Diligence: Examining the company’s financial statements in detail to ascertain its financial health and evaluating its position within the industry are all part of this process. You will reduce risk and make more educated decisions based on the results of thorough research.
- Diversification: Spread investments across various sectors, asset classes, and regions to reduce the impact of any single investment’s failure. Essentially, diversification operates on the principle of not putting all one’s eggs in one basket, ensuring that market volatility in one area doesn’t severely impact the entire portfolio.
- Skepticism: Maintain a healthy level of skepticism. Question claims and projections, especially if they seem overly optimistic without tangible backing. Skepticism in stocks involves approaching investment opportunities with a critical mindset, questioning assumptions, and not taking information at face value. It encourages thorough research and due diligence, ensuring that investment decisions are grounded in fact rather than emotion or market hype.
- Stay Informed: Regularly follow financial news to stay updated on industry trends, red flags, and potential warning signs. It also means continuously updating yourself with the latest market trends, company news, and economic indicators.
- Avoid Herd Mentality: Make investment decisions based on solid research and personal financial objectives, not merely on popular sentiment or trends. Avoiding herd mentality in stocks entails making investment decisions based on thorough research and individual analysis rather than merely following popular sentiment or trends. Succumbing to herd mentality can lead to inflated asset prices or market bubbles as investors collectively rush to buy or sell.
Finally, you need to accept that you will get things wrong, and sometimes being fooled is part of it. Just try not to make the same mistakes time and time again.
If you are interested in learning more about ideas from my company, The Edge, drop me an email at [email protected]
Read the full article here