Investment Thesis
According to the management, kiosks are the new stars of Shake Shack (NYSE:SHAK). You know, those shiny machines that let you order your yummy burgers and shakes without talking to anyone. Shake Shack is putting more kiosks in its stores because they think kiosks are better at selling more stuff than humans, and they also stop customers from tipping to improve labor efficiency. That’s really not that bad because Shake Shack pays its workers on average 19% more than other places.
Shake Shack Inc. reported 24.5% revenue growth driven by licensing revenue growth of 36.7%. SHAK stock was up 26% after earnings, and its YTD return was 59%. The stock is currently trading at $66.5 per share after being pulled back from a high of $125 per share in 2021 or a high of about $100 per share in 2019. The company raised its license openings and expected its adjusted EBITDA to grow by 78% in 2023. We believe the company can more effectively adapt to the environment given its position in premium fast food. Its overseas expansion strategy seems to be working. Its valuation was reasonable for us, considering its growth potential. We rate SHAK stock as “Buy”.
Key Takeaways from Q1 2023 Earnings:
- Shake Shack’s first quarter results in 2023 exceeded expectations, as the company reported increased sales growth, expanded margins, and disciplined expenses.
- The company experienced accelerated revenue growth and same-store sales growth from the previous quarter, driven by positive traffic of 4.8% and price increases.
- Restaurant level margins also increased significantly, to 18.3% from 15.2% in the first quarter of the previous year.
- Shake Shack raised licensed openings from 25–30 to 30-35, indicating positive future growth prospects.
- The company’s adjusted EBITDA is expected to grow by 78% in 2023.
Guidance (SHAK)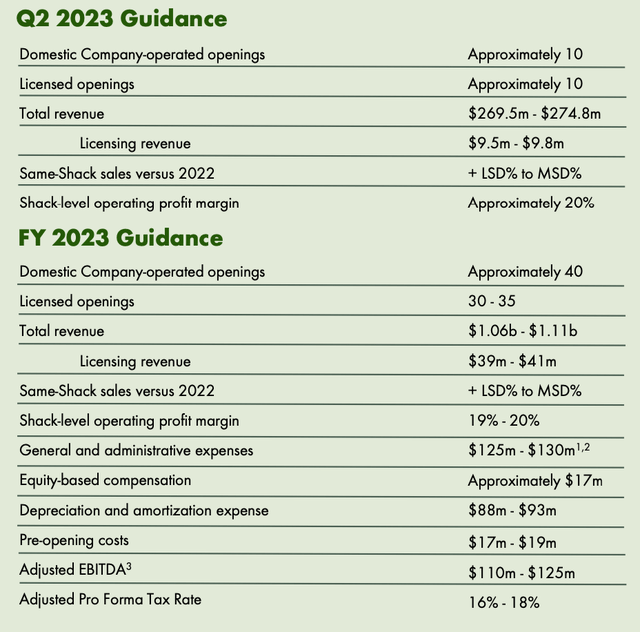
Fundamental Growth Drivers
The licensing business expanded globally
The success of its licensing business provides much upside for the company, as it shows that Shake Shack’s brand is recognized worldwide and that its business model is scalable overseas. The company’s global strategy relies on licensing and partnering with local suppliers to ensure fresh and quality ingredients. It focuses on expanding in metro areas where we believe the supply chain risk is low. Additionally, this success can provide visibility into future revenue streams and offer protection from macroeconomic downturns.
Its new store openings achieved over 30% cash-on-cash returns measured in the third year of operation.
One particular area of exceptional growth for licensing businesses is China, and the company is expanding its reach globally.
Despite their success, the management team has recently announced that they expect to slow their growth from the low teens in Q1 to the low to mid single digit range in 2023.
Although the company’s guidance reflects a modest degree of slowing, there is still a path to exceed it if the consumer remains healthy. In an effort to achieve this goal, the company plans to increase its system-wide shack count by around 70 to 75 units this year, with same-shack sales expected to grow in the low to mid single digits. The company’s success in over-indexing to higher-income consumers and its expensive LTO, white truffle, give it a strong foundation to build upon in this challenging environment.
SG&A leverage
Shake Shack had a reputation for offering a great culture for team building, and its employee compensation was higher than the industry average. In the Seattle area, Shake Shack paid its employees an hourly wage of $15.4, which was 19% higher than the median hourly pay of $15.44 for restaurant staff in the U.S. This high pay allowed Shake Shack to attract and retain skilled workers, which ultimately led to a more efficient and productive team. Additionally, Shake Shack’s emphasis on team building and creating a positive work environment helped foster a strong sense of community among its employees, further contributing to its success as a company.
Average salary of Shake Shack (Indeed)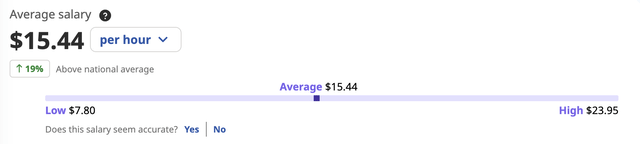
Risks
Financials (SHAK)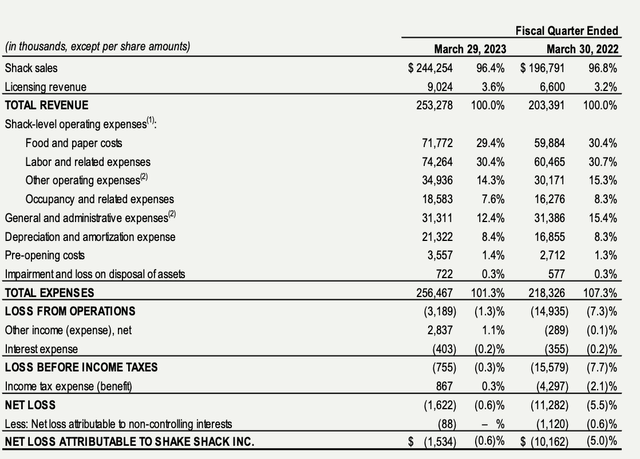
Shake Shack closely monitored its expenses and prices in order to maintain a high restaurant margin outlook. However, according to the management, the company faced several risks, particularly consumer demand uncertainty and inflation. Its cost of goods sold is expected to increase by mid- to high-single digits, with beef being the largest risk factor.
Shake Shack’s supply chain focused on using premium ingredients, which were subjected to fluctuations in commodity prices. Despite inflationary pressures, the company plans to navigate these challenges and maintain higher operating profitability through cost saving initiatives going forward.
Valuation
Valuation multiple (Seeking Alpha)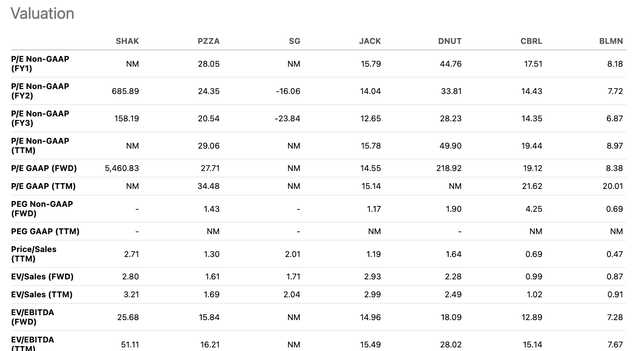
Growth comparison (Seeking Alpha)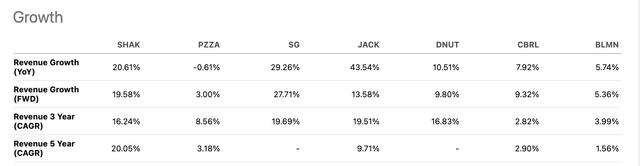
Its forward EV/Sales ratio was slightly higher than its peers’. The market expected the company to grow its revenue by 19% in 2023. Additionally, the management provided EBITDA guidance to grow by 78%, significantly outperforming most of its peers.
Shake Shack’s burgers were often compared with those of Five Guys and In-N-Out. Since Shake Shack’s burger unit price is more comparable with Five Guys’, we will use Five Guys as our benchmark.
Burger Price Comparison (Five Guys, Shake Shack and In-N-Out)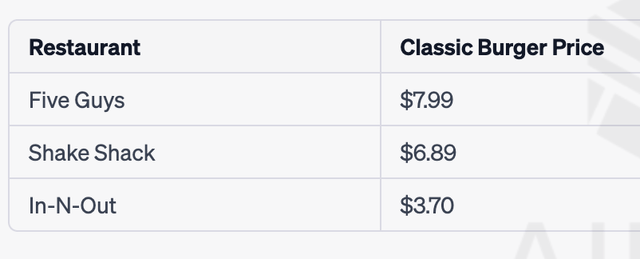
Shake Shack now had 449 stores (domestic 295 and international 154), while Five Guys had 1,432 stores in the U.S. The restaurant industry is highly fragmented and is still growing. Hence, we think Shake Shack definitely has room to grow, especially in the metro area.
Thus, we believe the market has not fully priced in the potential for the company to outperform its peers and meet guidance. Overall, we saw great upside potential in this company and believed that it was an attractive investment opportunity.
Catalysts
We think Shake Shack has upside in the U.S., even in this inflationary environment. Its potential in the international market was even stronger. The company raised its guidance for licensed openings to 30-35, indicating better than expected future growth prospects. We believe new store openings and licensing business growth are catalysts for the stocks.
Read the full article here