Artificial Intelligence (“AI”) and generative AI such as ChatGPT necessitate the need for substantial memory and storage capabilities for the storage of extensive datasets, training intricate models, and handling vast volumes of data processing.
Nvidia (NVDA) is the poster child of AI and generative AI through its GPU chips. GPUs are highly parallel processors designed for tasks like graphics rendering and general-purpose computing. In a data center, GPUs are increasingly used for accelerating complex computations, such as machine learning, deep learning, and scientific simulations.
But the storage of these extensive datasets is done through Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid State Drives (SSDs). HDDs and SSDs store the large datasets required for training generative AI models. HDDs provide high-capacity storage at a lower cost, while SSDs offer faster data access speeds. Data Retrieval: Fast data retrieval from SSDs significantly reduces the time it takes to load training data into memory for processing. This minimizes training bottlenecks caused by slow data access.
HDD Analysis
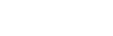
Graphically, I compare HDD data for Seagate (NASDAQ:STX) and Western Digital (NASDAQ:WDC) companies in Chart 1, which shows two important metrics, according to The Information Network’s report entitled The Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD) Industries: Market Analysis And Processing Trends:
- The top two lines compare Nearline Data Center HDDs shipments for Seagate (gray line) and Western Digital (red line) between F2Q19 and F4Q23.
- Nearline HDDs are known for their high storage capacities. They are often used in data center environments and enterprise storage systems to store large amounts of data that doesn’t need to be accessed as frequently as data stored on SSDs.
But the key is the drop in HDD shipments starting in F4Q23. For Seagate, it shows a significant drop in F3Q23 of 8.9% in nearline followed by a F4Q23 drop of 37.0%. It compares to a F3Q23 increase of 31.1% for WDC followed by a F4Q23 decrease of 25.6%. Trendlines (dotted lines) for both are positive but growth is stronger over this period for Seagate.
The Information Network
Chart 1
NAND SSD Analysis
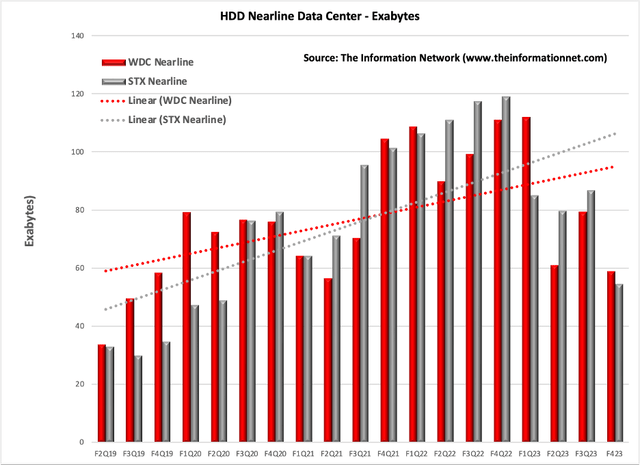
NAND flash storage in the form of SSDs has revolutionized server storage by providing improved speed, reliability, and efficiency compared to traditional hard drives, contributing to enhanced server performance and data center capabilities. Chart 2 shows SSD shipments for servers between Q1 2020 and Q2 2023. Note that this is for all SSD suppliers, not just STX or WDC.
NAND SSDs reached their peak in 4Q 2021 and continued to decline until increasing in the recent 2Q 2023. But the decline in SSD shipments have not been as significant as HDDs in Chart 1.
The Information Network
Chart 2
Nvidia Vs Western Digital Revenue Analysis
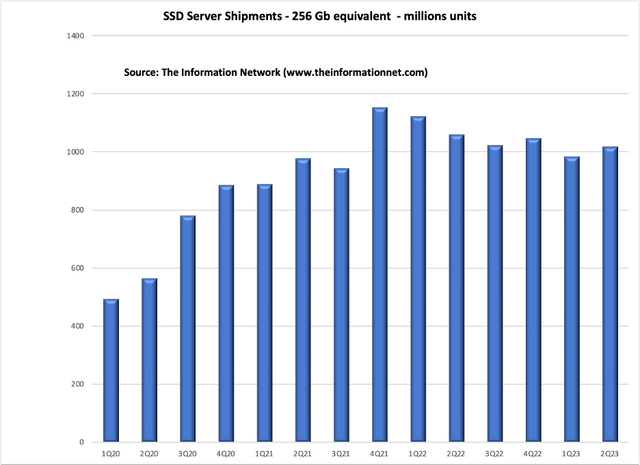
Chart 3 shows Data Center revenues for Nvidia between FQ1 2018 and FQ2 2023. As with SSDs in Chart 2 above, revenues peaked and then remained flat. But unlike SSDs or HDDs in Chart 1 above, Nvidia exhibited explosive growth in FQ2 2023 ending July 2023.
Importantly, Nvidia’s data center division recorded a whopping 140% QoQ growth and the company provided guidance for another 20% QoQ growth for Q3. The data center products coming from Nvidia, as well as AMD (AMD) and others, means more storage demand, and products coming from STX and WDC will be major beneficiaries.
The Information Network
Chart 3
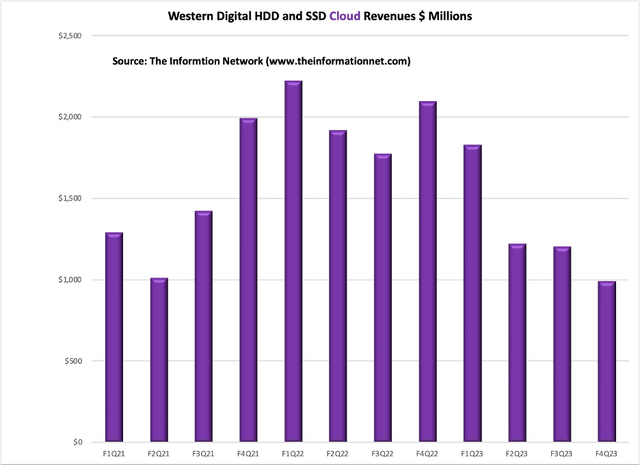
In comparison, Chart 4 shows Western Digital’s Cloud Revenues for the period Q1 2021 through Q2 2023, and are a combination of HDD and SSD revenues. Western Digital manufactures both storage types.
Cloud represented 37% of total revenue in FQ4 2023, according to WDC’s latest earnings call press release. Sequentially, the decline was primarily due to a decrease in capacity enterprise drive shipments. Nearline bit shipments were 59 exabytes, down 26% sequentially, driven by ongoing weakness at cloud customers. The year-over-year decrease was primarily due to declines in both hard drive and flash product shipments. WDC doesn’t separate cloud HDDs from SSDs.
For fiscal year 2023, Cloud represented 43% of total revenue. The year-over-year decrease was primarily due to reduced shipments of capacity enterprise hard drives and enterprise SSDs.
The Information Network
Chart 4
Investor Takeaway
Generative AI such as ChatGPT can produce a wide variety of content, including text, images, videos, and more. As organizations leverage these models to create content for marketing, design, virtual environments, and other applications, they will need to store the generated content. This can lead to a substantial increase in the volume of data that needs to be stored in cloud servers and data centers.
For training generative AI models, diverse and extensive datasets are required. Organizations might collect and store large datasets to train these models effectively. These datasets may consist of text, images, videos, and other types of data, contributing to increased storage demands. For example, nearly four million videos are uploaded daily to YouTube and their file sizes can be thousands of times larger than a single image. Platforms like YouTube need data centers with massive storage arrays to accommodate this volume of content.
The major storage beneficiaries are Seagate and Western Digital. Flash storage will continue to support high-performance computing systems, while large-capacity HDDs will remain the most economically viable storage solution for storing the immense amounts of data generated and utilized for predictive analytics.
According to The Information Network’s report entitled The Hard Disk Drive (“HDD”) and Solid State Drive (“SSD”) Industries: Market Analysis And Processing Trends, more than 90% of exabytes in cloud data centers are stored on HDDs, and the remaining 10% are stored on SSDs.
HDDs continue to offer approximately five times better cost efficiency per bit compared to equivalent flash solutions, and we anticipate this difference to persist through the end of the decade.
Looking ahead, HDDs are expected to maintain market share, thanks in part to advances that continue to increase capacities while maintaining performance. I forecast that HDDs are well-positioned to dominate data centers for the next 10 years.
For example, Seagate’s HAMR (Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording) and WDC’s MAMR (Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Recording) are advanced technologies designed to enhance the storage capacity and performance of hard disk drives (HDDs), a type of data storage device that uses spinning disks to store information magnetically. Both HAMR and MAMR aim to overcome the limitations imposed by the superparamagnetic effect, which becomes significant as data bits are packed more densely on HDD platters.
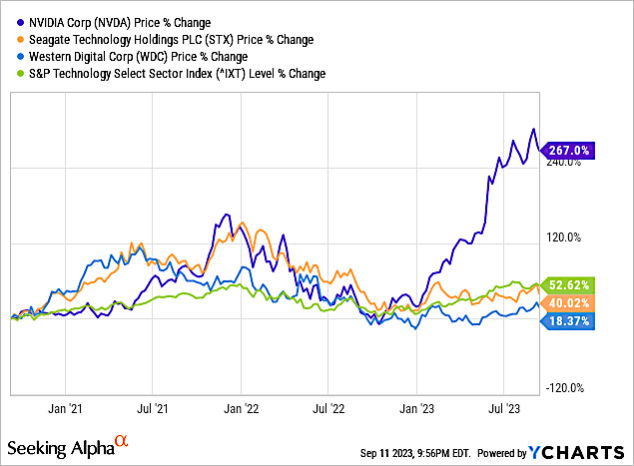
Chart 5 shows that since the beginning of 2023, there has been a bifurcation in share price between Nvidia, Seagate, and Western Digital. This disconnect in share price will get smaller as demand for storage products will be strong. Chart 5 shows share price changes for a 3-year period. I added the S&P Technology Select Sector Index (IXT) as a check for performance of STX and WDC.
YCharts
Chart 5
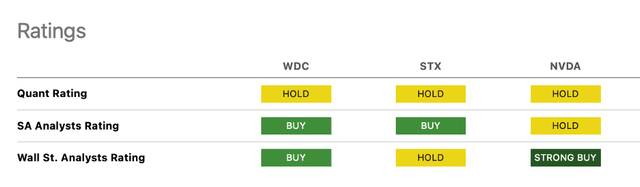
Quant Ratings in Chart 6 show a Hold for all three companies, with Wall St. Analyst Ratings showing a Buy for WDC, a hold for STX, and a Strong Buy for NVDA.
Seeking Alpha
Chart 6
My rankings follow the Quant in Chart 6. I have a Hold on all three – STX and WDC because of headwinds at the data center, and NVDA because of high valuation and would wait for a correction.
Clearly, any company with an “AI” in the title or business plan has been performing strongly YTD. It was my contention that STX and WDC have a symbiotic relationship with NVDA and AI, and I expect share prices to start ramping once investors are made aware of this.
I had already discussed a similar relationship between NVDA and memory companies and the demand for HBM packages for the generative AI sector, as I wrote in a July 20, 2023, Seeking Alpha article entitled “Micron Losing Ground In DRAM In HBM And 128GB DDR5.”
Read the full article here