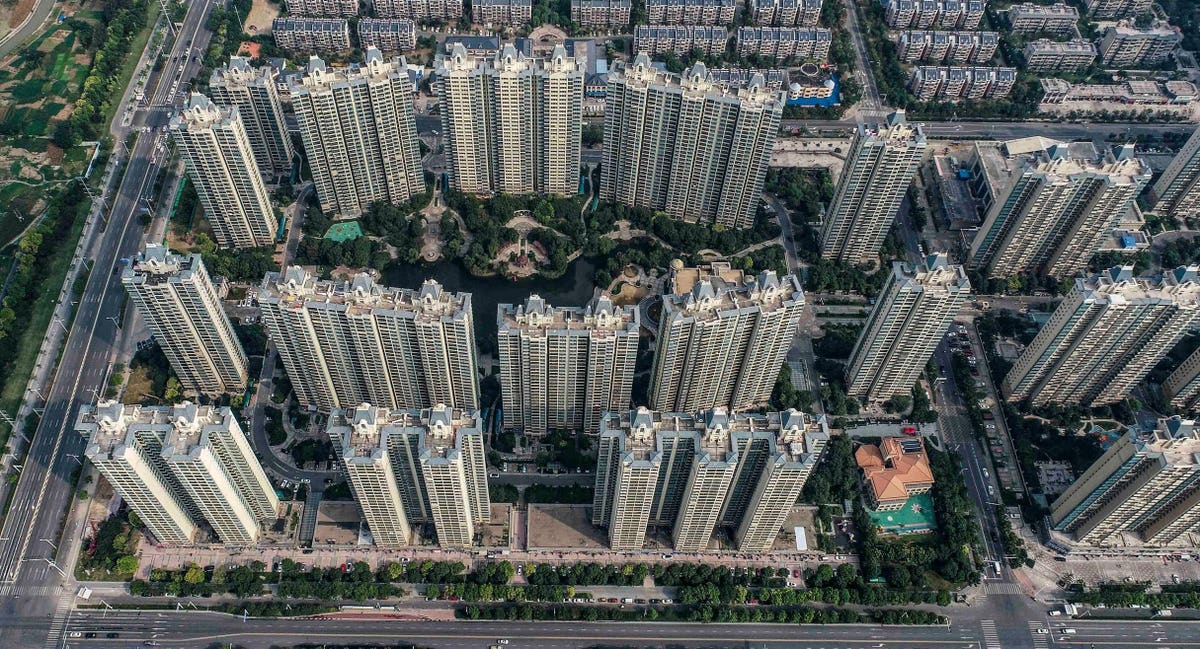
Days after Chinese real estate developer (and EV battery manufacturer) Evergrande filed for bankruptcy in New York City, Washington held a hearing on Monday about the impacts the China debt crisis might have on the U.S.
Evergrande has long been a sore spot for China debt watchers. Now that it’s officially admitted it’s broke, China bears can say, “I told you so.”
Evergrande has $28.1 billion in outstanding bonds. At one point, BlackRock
BLK
For a hearing centered on the risks to the U.S. of China’s debt crisis, at no point during today’s U.S. China Economic and Security Review Commission hearing did anyone wonder out loud if the government was prepared to bail out Wall Street in the eventuality of more China bankruptcies. We will have to save such a slap-in-the-face moment for when it happens. From what I know about the Commissioners, none would advise Congress to allow that.
In hearings like this all year, it is clear that Washington wants the market to know China is riskier than ever. When Evergrande chokes, DC sees the opportunity to make its case to “de-risk”.
Monday’s hearing was planned before Evergrande filed Chapter 15.
Nicholas Borst, director of China research at Seafarer Capital Partners in California, was one of three witnesses at the hearing. He said he visited 10 different Chinese cities this year and noted that growth “fell sharply in 2022 due to lockdowns”.
He said China’s economic activity is also “substantially weaker than they predicted. They are in danger of losing their economic momentum. There’s been a failure to crack down on real estate leverage and to prepare for the post-pandemic era,” Borst told the Commission. “The property market remains weak.”
This sets the stage for more Evergrandes, perhaps dozens of smaller ones in a worse case scenario.
China’s problems are centered on debt, but much of the debt issue centers around shadow banking in the provinces, a massive credit expansion in 2008-09, and their forever real estate bubble.
Real estate is imperative for China’s middle class because it is the only place they can save, other than local securities or savings accounts. The stock market is more of a gambling den in China, and seen as short-term. Real estate is seen as more sound, and long-term. This and provincial leaders’ interest in full employment and infrastructure make real estate a major economic driver.
Adding to these challenges is the official 21.3% unemployment rate for Chinese youth, many of which lost jobs at small to midsized businesses killed from lockdowns. Bad data has led China’s government to stop sharing economic figures that highlight weakness, Bloomberg reported.
For on-the-ground sentiment, it is worth noting that during Covid, private Chinese businesses were met with a “regulatory storm” which saw the implanting of Communist Party staffers inside the boardrooms and advisory teams.
Less debt, plus tighter security and control are replacing the China growth story.
The Debt Crisis: How Bad Is It?
China is a black box for information. Due diligence is not easy. Here is what is known, according to witnesses at today’s hearing.
China’s government debt to GDP is low, around 30%. But overall debt, which includes all those second and third mortgages, corporate debt and massive provincial government debt, is about three times that of China’s GDP. Same as the U.S.
“It’s normal for an advanced economy to have high levels of debt, but China has rich country levels of debt with middle-income levels of GDP, so that is one problem,” said Borst. “The other problem is the structuring of debt,” he said, adding that Beijing isn’t broke, but the provincial governments are getting there. That would be the equivalent of Washington having money but the 50 states being within varying degrees of broke.
“The provincial governments used to make a lot of money from off-balance sheet vehicles, shadow banking to borrow and spend, and more importantly, real estate. It’s all credit related, with insufficient revenues coming in to pay that debt off. Until that is resolved, I’d be very pessimistic,” Borst said.
Over the past month, a suite of new private sector reforms were introduced. China knows it cannot grow entirely through state companies, but the party committees inside these companies are like a third wheel. “I think they are going to turn to the old playbook,” Borst said. “They’re going to be building new infrastructure, even if the country doesn’t need it.”
The China consumer-led growth story isn’t happening. China is still as poor as Brazil and outside of the big tier one cities, even poorer. China consumption is roughly 40% of GDP versus 60% on average for the rest of the world.
No one is talking about a province going broke. And no one gave the names of potential new companies to follow Evergrande at the hearing today.
On Monday, China’s Central Bank (PBOC) decided to keep a long-term rate unchanged and only cut its short-term rate to 3.44% from 3.55%. This will barely help the roughly ¥800 billion ($109 billion) of short-term debt.
“To refinance these large debts with lower interest rates, China can use the PBOC balance sheet,” said Logan Wright, partner and director of China Markets Research for the Rhodium Group.
The PBOC has around $3.5 trillion in reserves, basically the entire output of the Brazil and Russia economies combined in its foreign currency reserves account. China may do this in a worse case, but the PBOC has showed no interest in ever using those funds to pay off debt.
Wright thinks it’s a possibility now, owing to the severity of the crisis.
“Maybe you let a few default before coming in with a rescue package. We are in unchartered waters,” he said. “I think we will see a reactive plan in the next six to 12 months, rather than something more pro-active.”
China investors have been trying to better understand the debt situation since at least 2011 following massive spending and credit in the Great Recession years.
Commissioner Kim Glas asked if the U.S. was one step ahead and prepared for more Evergrande-like blowups. “I’m thinking not just in terms of the risk to investors but to our economic sectors here at home,” she asked.
Borst had the best response.
“Despite the slowdown in trade between the U.S. and China, China is a key export market for the U.S. and their slowdown will impact a lot of companies,” he said. Borst invests in China, both client money and his own money.
“China is an investment market for a lot of firms, and that will mean lower returns for a lot of investors here,” he told the Commissioners. “China has been the heart of growth in Asia. If it slows, as we are predicting, it will also hurt other countries in the region that have huge economic ties to them. The growth miracle is over. You either get a soft landing of 3% if they handle this well; or if they don’t, growth would be much lower than that.”
As far as other Evergrandes, the value of the Chinese housing stock is hard to know for sure. Statista puts it at $113 trillion. A Reuters article this week put it at $62 trillion.
“Whatever the reality, it’s a very big number,” warned Brian McCarthy, head of research at Macrolens, an investment research firm based in Massachusetts.
China’s debt “is in the process of being haircut by a very large amount. The official home price data have always been nonsense. But check out the back of this envelope: If the housing market is worth $62 trillion and it’s going to get a conservative estimated haircut of 30%, then we’re talking about an $18 trillion decline in asset values,” McCarthy said. “That’s a loss of 100% of China’s GDP that someone will have to be saddled with. That process is underway, but we are still in the early innings.”
The U.S. China Economic and Security Review Commission a two-panel discussion today. The first one was on investor risks in the Chinese economy, and the second panel discussed supply chain risks of manufactured goods.
Congress created the Commission 23 years ago to monitor and investigate the national and economic security implications of doing business with China.
Read the full article here