Velo3D (NYSE:VLD) is an additive manufacturing company focused on enabling the production of high value metal parts. Its business is currently small but growing rapidly based on its ability to print metal parts with complex internal geometries. Velo3D is still trying to establish its business though, and as a result margins are currently poor. In addition, the production of high value metal parts is fragmented, and the technology landscape continues to evolve. These factors make Velo3D’s stock highly speculative, particularly given the expectations the current valuation implies.
Market
Velo3D is targeting mission critical components for customers where the cost of failure is high. This is a potentially attractive strategy for leveraging the company’s technology, and could result in relatively high margins, which has been a problem for additive manufacturing vendors in the past. High value metal parts also provide a large opportunity, which has estimated to be in excess of 100 billion USD. While the market is large, it only offers modest growth and is also highly fragmented, with the largest players having less than 10% (PCC) and less than 5% (Howmet) market share globally.
Figure 1: High Value Metal Parts Market (source: Velo3D)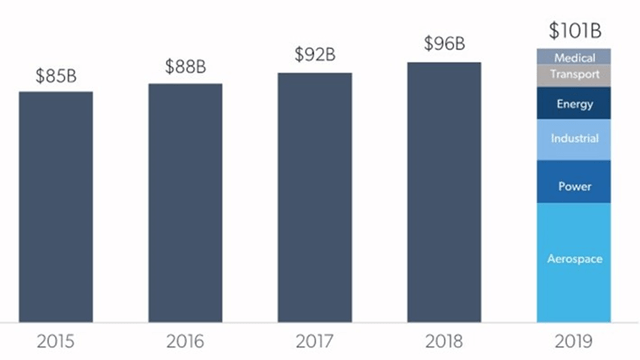
Velo3D believes that the high value parts market is primed for disruption by additive manufacturing for a number of reasons:
- Manufacturers are willing to pay a premium
- Additive manufacturing enables shorter lead times
- Additive manufacturing is cost competitive with incumbent technologies
- Additive manufacturing enables the production of complex parts that would be difficult to machine
There is interest in utilizing additive manufacturing for producing metal parts, but adoption is currently low. Additive manufacturing enables complex assemblies to be consolidated into a single part and can also shorten lead times and reduce costs. Existing metal additive manufacturing technologies have struggled to produce some designs though due to the need for support structures. Velo3D’s technology obviates this need and as a result could help accelerate adoption.
Figure 1: High Value Metal Part Additive Manufacturing Market (source: Velo3D)
Velo3D
Velo3D is a metal additive manufacturing company that provides solutions for producing high value metal parts, including hardware, software and services. It wants to capture market share by offering high performance, short lead times and low costs.
Velo3D’s printers enable the accurate production of complex geometries and incorporate unique capabilities such as the ability to print without support structures, ensuring better part integrity and reduced post-processing requirements.
In addition to hardware, Velo3D offers software solutions that optimize the printing process. Its software suite includes tools for design preparation, simulation, and process control, enabling engineers to efficiently create and validate parts before printing.
Velo3D’s products include:
- Flow – Print preparation software
- Sapphire – Metal AM printers
- Assure – Quality validation software
Velo3D has been ramping production of its Sapphire XC and Sapphire XC 1MZ products in recent periods to meet increased demand. These units allow larger parts to be manufactured and are targeted at mass production.
Figure 3: Velo3D Product Portfolio (source: Velo3D)
Velo3D uses Laser Powder-Bed Fusion, which is the same method used by 95% of the metal additive manufacturing market. Incumbent technology generally requires the use of supports though. These supports may be internal and inaccessible, preventing the production of parts with complex internal geometries. Velo3D’s technology avoids the need for supports, allowing the creation of designs with complex internal geometries. Support free printing is enabled by a combination of software, hardware and printing processes. This appears to be about process knowledge as much as specific hardware or software capabilities.
Velo3D primarily serves industries with demanding requirements, such as aerospace, oil and gas, and power generation. Its technology is particularly valuable for manufacturing complex components that are difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods, offering benefits like weight reduction, improved performance, and streamlined supply chains.
Figure 4: Velo3D Customers (source: Velo3D)
Competition
Velo3D faces a range of competitors, both in the additive manufacturing space and from incumbent subtractive manufacturing approaches. While continued improvement in additive manufacturing technology should lead to the displacement of approaches like machining for some applications, there is uncertainty regarding the best additive manufacturing technology and service provider.
- EOS offer a range of solutions, with PBF being the company’s technology of choice for metal additive manufacturing. EOS is a well-established company with a long history in additive manufacturing.
- General Electric (GE) offers additive manufacturing systems, materials, and software solutions through its GE Additive division.
- SLM Solutions is a German company specializing in metal-based additive manufacturing systems. It offers machines that utilize PBF technology.
- Renishaw is a global engineering and technology company that provides metal additive manufacturing systems based on PBF technology.
- 3D Systems (DDD) offers a broad range of additive manufacturing 3D solutions, including both metal and plastic systems.
- Desktop Metal (DM) offers a range of additive manufacturing solutions, with its metal technology based on binder jetting. Desktop Metal is focused on mass production and its business has been scaling rapidly.
Most of these vendors have similar offerings, with Velo3D being differentiated by its ability to produce support free parts. Desktop Metal and Markforged are differentiated by their use of binder jetting or metal filled FDM. Desktop Metal claims far greater throughput and lower costs than competing approaches, although Velo3D is dismissive of the technology.
Figure 5: Metal Additive Manufacturing Technology Comparison (source: Velo3D)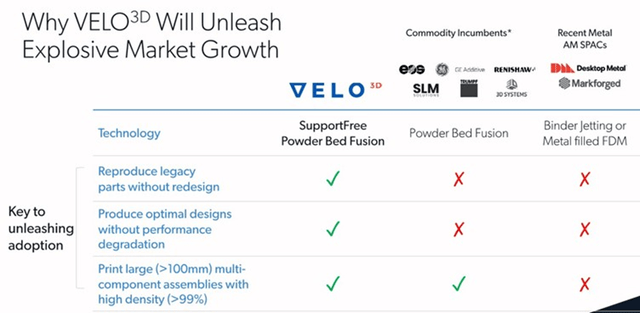
Financial Analysis
Despite a weak macro environment, customer demand has remained robust so far and as a result Velo3D is rapidly scaling its business. Revenue more than doubled in the first quarter of 2023 to 27 million USD. Bookings increased more than 30% sequentially to 20 million USD and Velo3D’s backlog at the end of the first quarter was 24 million USD.
Velo3D’s backlog declined in the first quarter, which was attributed to the removal of an order where the customer hasn’t been able to demonstrate adequate progression in securing financing to complete the purchase. This order is responsible for approximately 80% of the decline in backlog.
Figure 7: Velo3D Revenue (source: Created by author using data from Velo3D)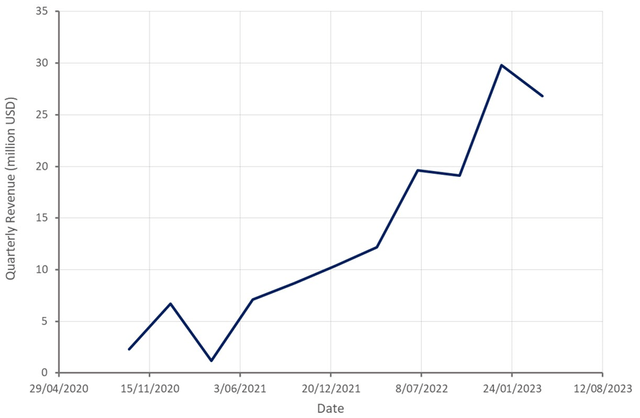
Velo3D is transitioning from upfront sales to a recurring revenue model, although the effort is still fairly nascent. Recurring revenue increased from 2 million USD in the first quarter of 2022 to 2.2 million USD in the first quarter of 2023.
The recurring revenue model may be helping to offset demand headwinds in an environment where customers are generally reluctant to make capital investments. This model creates its own headwinds though, as less revenue is received upfront. The recurring revenue estimate in the figure below is based on a 60,000 USD annual service fee, 50 USD per hour royalties and 5,800 hours of operation per year.
Figure 6: Sales Model Financials (source: Velo3D)
Revenue guidance for the second quarter of 2023 is 25-29 million USD and bookings are expected to be 23-29 million USD. For the full year, revenue guidance is 120-130 million USD, with 100-130 million USD bookings. While growth is still currently robust, this guidance indicates that growth is expected to rapidly decelerate. Whether Velo3D can meet its mid-term revenue goals remains uncertain but in the current demand environment this seems unlikely.
Figure 8: Velo3D Revenue Forecast (source: Velo3D)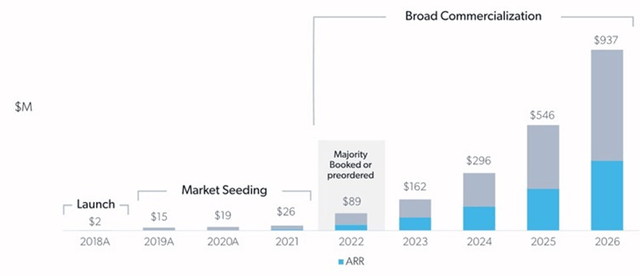
Velo3D’s gross margin remain close to zero and are yet to show an improvement with scale. It is probably too early to draw any conclusions from the company’s current margins. Velo3D is still implementing basic process improvements to reduce production cycle times and waste, improve inventory controls and the productivity of labor.
Figure 9: Velo3D Profit Margins (source: Created by author using data from Velo3D)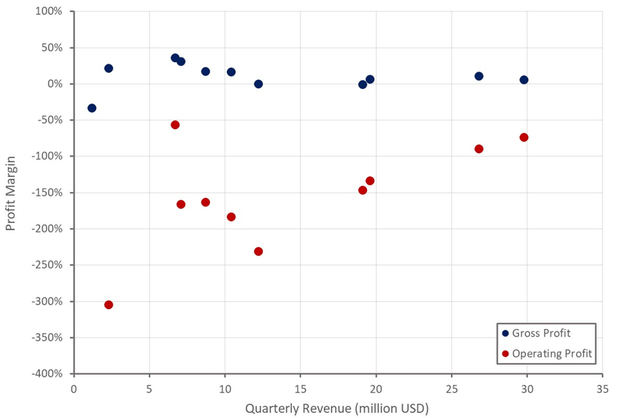
Velo3D is driving gross margin expansion through:
- Reduced material costs
- Improved manufacturing efficiency
- Economies of scale
- Higher ASPs through price increases and product mix
Material costs are expected to decline as Velo3D shifts to new long-term, low-cost supply contracts. This will take time to impact the income statement though, as some of these contracts are still being implemented or negotiated. For contracts already in place, lower costs will also still need time to flow through inventory. Gross margins are expected to be 12-16% in the second quarter of 2023, improving to 30% in the fourth quarter.
Figure 10: Velo3D Unit Economics (source: Velo3D)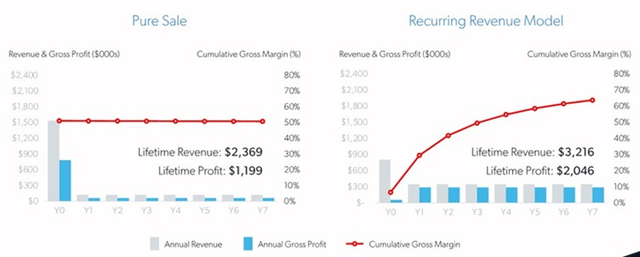
Valuation
Based on a revenue multiple, Velo3D’s stock looks quite expensive as the business is immature and expanding rapidly. This doesn’t necessarily make the stock overvalued though as Velo3D is targeting a large market and has a relatively differentiated offering.
Paying a high multiple for an additive manufacturing company is a risky proposition though. The market has generally offered limited growth in the past and most companies have struggled to generate positive free cash flows. Despite this, the market is maturing and a recent wave of consolidation may lead to better industry dynamics going forward.
In Velo3D’s case, it is targeting markets which may be supportive of higher margins. Buyers may be willing to pay a premium in high value applications where the cost of the part is generally low relative to total costs. Additive manufacturing may also be at a cost advantage in many of Velo3D’s target markets, enabling mass production. These positives are tempered by the fact that customers in many of Velo3D’s end markets are fairly concentrated, and hence may have significant bargaining power.
In addition, the size and sustainability of Velo3D’s competitive advantage is unclear. A number of competitors already claim to be able to do support free printing. Additive manufacturing technology is also still evolving, and any advantage may yet prove to be fleeting.
Figure 11: Velo3D Relative Valuation (source: Created by author using data from Seeking Alpha)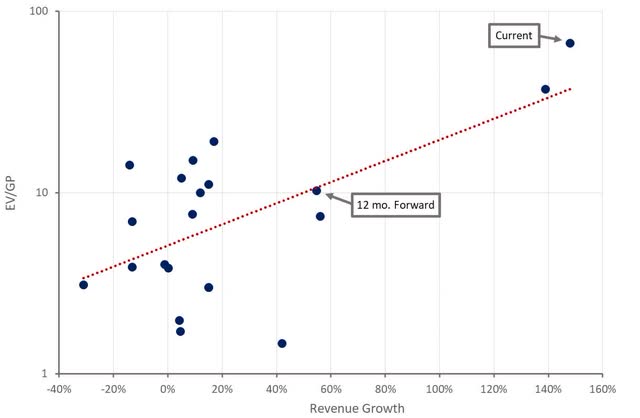
Read the full article here